
CNAPP Solution Buyer’s Guide: Make Informed Decisions About Your Organization’s Cloud Native Security
To protect your cloud-native applications, you need to choose the right security solutions for your organization use. A Zero Trust CNAPP (Cloud Native Application Protection Platform) is a good option, as it can provide comprehensive security for your applications. When choosing a CNAPP security platform, you need to consider your organization’s specific security requirements. Some factors to consider include the types of applications you use, the cloud platforms you use, and your budget.
Reading Time: 13 minutes
Table of Contents
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, securing cloud native applications has become a paramount concern for organizations worldwide. As the adoption of cloud technologies accelerates, so does the need for robust security measures to safeguard sensitive data and mitigate evolving threats.
CNAPP (Cloud Native Application Protection Platform) is an innovative security solution that provides comprehensive protection for cloud native environments, from vulnerabilities and unauthorized access.
💡TL;DR
- A complete security and compliance solution for cloud native applications, CNAPP combines infrastructure scanning, runtime cloud workload protection, container scanning, security posture monitoring, and security posture management.
- Protection against unwanted access, data breaches, and other dangers is provided via its zero-trust design.
- Application security focuses on protecting the application layer. Data encryption, vulnerability scanning, and intrusion detection are all components of protection. Protecting cloud applications is made easier with AccuKnox.
- For Kubernetes deployments, KSPM is a zero-trust security platform that identifies vulnerabilities, keeps an eye on resources, and gives visibility into containerized workloads.
💡What exactly is CNAPP?
Gartner defines it as “a unified and tightly integrated set of security and compliance capabilities designed to secure and protect cloud native applications across development and production. CNAPPs consolidate a large number of previously siloed capabilities, including container scanning, cloud security posture management, infrastructure as code scanning, cloud infrastructure entitlement management, runtime cloud workload protection and runtime vulnerability/configuration scanning.”
At the intersection of cloud native development and security, CNAPP offers a revolutionary approach that goes beyond traditional security paradigms. Its zero-trust architecture and comprehensive set of features empower organizations to embrace cloud native applications with confidence, enabling the seamless deployment of innovative solutions while maintaining a robust security posture.
Understanding CNAPP
Traditional security approaches are often ill-equipped to handle the unique challenges posed by these dynamic and rapidly evolving environments. This is where the Cloud Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP) comes into play.
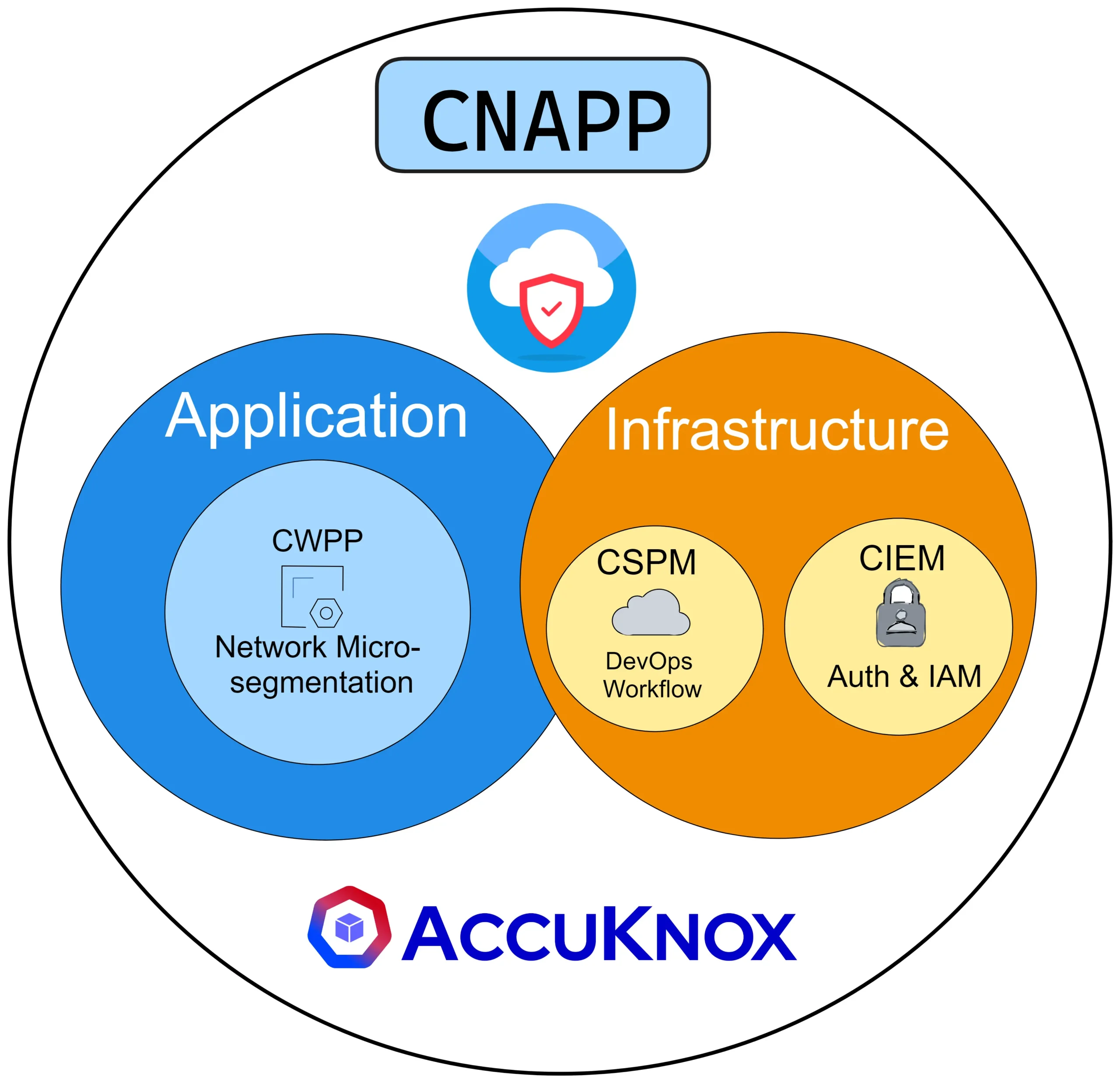
The Objective of CNAPP
CNAPP’s primary objective is to address the security problems that arise when deploying and managing cloud native applications. By adopting a zero-trust architecture, CNAPP establishes a robust security foundation that ensures comprehensive protection from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other potential threats. With CNAPP, organizations can confidently embrace cloud native technologies, knowing that their applications are shielded from vulnerabilities and cyber-attacks.
Security Problems Solved by CNAPP
Cloud native environments introduce a myriad of security challenges due to their distributed nature, dynamic infrastructure, and reliance on microservices architecture. These challenges include container vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, unauthorized access, compliance risks, and runtime threats. Addressing these issues requires a holistic security solution like CNAPP that is specifically designed for cloud native environments.
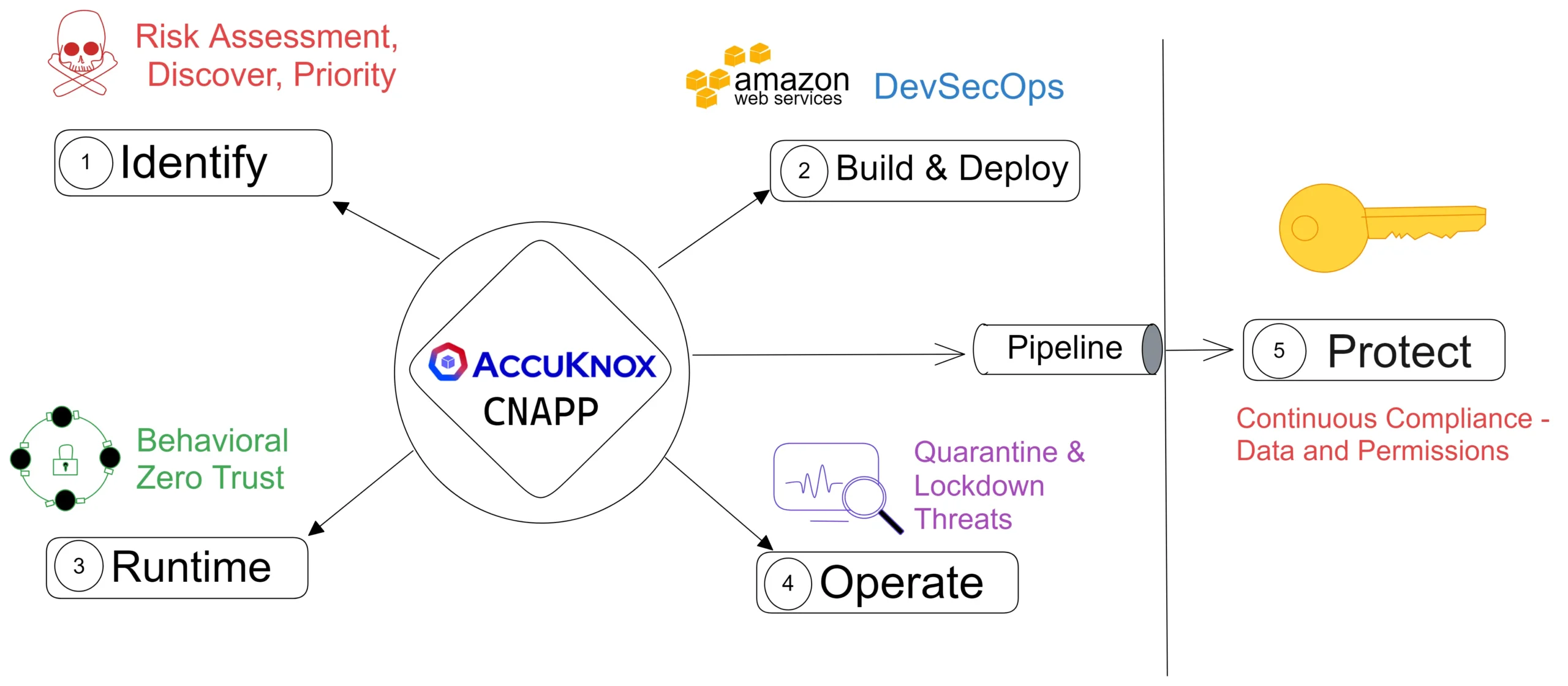
How CNAPP Helps Mitigate These Challenges
CNAPP offers a comprehensive set of features to address security challenges in cloud native applications.
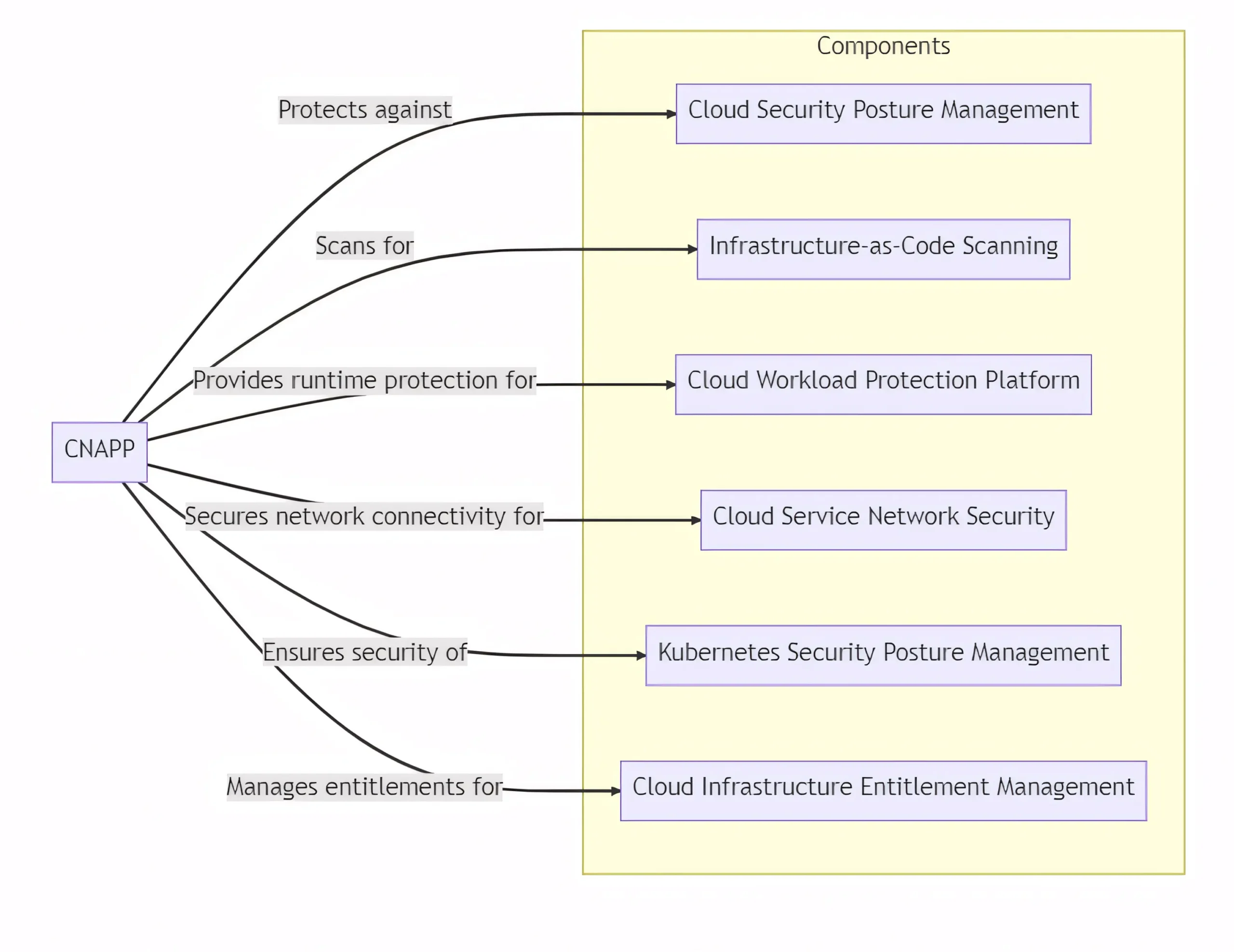
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): Proactively identifies and resolves misconfigurations, ensuring compliance with industry standards.
- Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) Scanning: Detects security risks in infrastructure provisioning scripts, minimizing potential attack surfaces.
- Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP): Provides runtime protection against threats, employing advanced techniques like behavioral analysis.
- Cloud Service Network Security (CSNS): Secures network connectivity between cloud services, enforcing granular access controls and encryption.
- Kubernetes Security Posture Management (KSPM): Ensures the security of Kubernetes clusters and workloads, following best practices.
- Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM): Manages entitlements and permissions for cloud resources, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
| Cloud Native App Exploit | Security Problem | Money Lost (Approx.) | How CNAPP Could Have Helped |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Breach | Weak authentication mechanism allowed unauthorized access to sensitive data | $1.5 million | CNAPP’s robust authentication and access control features could have prevented unauthorized access and protected the sensitive data. |
| Ransomware Attack | Inadequate backup and recovery measures led to data encryption and demanded ransom | $2.8 million | Cloud workload protection platform (CWPP) could have detected and mitigated the ransomware attack, preventing data encryption and minimizing financial losses. |
| API Vulnerability | Exploited API vulnerability exposed confidential customer data | $500,000 | Cloud service network security (CSNS) could have enforced granular access controls and encryption, preventing unauthorized access to the API and protecting customer data. |
| DDoS Attack | Lack of network security measures resulted in a massive DDoS attack, causing service disruption | $1 million | Cloud service network security (CSNS) could have detected and mitigated the DDoS attack, ensuring uninterrupted service availability. |
| Insider Threat | Insider leaked sensitive company information to a competitor | $3.2 million | Cloud security posture management (CSPM) could have continuously monitored and alerted on unauthorized data access, preventing the insider threat and reducing financial losses. |
| Misconfigured Storage | Misconfigured cloud storage exposed customer data to the public internet | Cloud security posture management (CSPM) could have detected and remediated the misconfiguration, preventing the exposure of sensitive customer data. | |
| Container Escape | Exploited container vulnerability allowed unauthorized access to the host system | $1.1 million | Kubernetes security posture management (KSPM) could have identified and patched the container vulnerability, preventing unauthorized access and financial losses. |
| Account Takeover | Weak password policies enabled hackers to take over user accounts | $700,000 | CNAPP’s robust authentication mechanisms, including multi-factor authentication (MFA), could have prevented the account takeover and protected user accounts and financial assets. |
CNAPP could have helped avoid these exploits by providing advanced security features such as robust authentication, access control, continuous monitoring, vulnerability detection, encryption, and proactive remediation. Its comprehensive set of capabilities would have mitigated the security problems involved and significantly reduced the financial losses incurred by these cloud native app exploits.
A Breakdown of CNAPP Components: Safeguarding Cloud Native Applications
Based on the Gartner innovation insight report, the Cloud Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP) can be broken down into four key components: Cloud native, Application, Protection, and Platform.1. Cloud Native
Focuses on the unique characteristics and architecture of applications built for cloud environments. It emphasizes leveraging cloud native technologies and principles to develop, deploy, and manage applications. Examples include:
a) Containerization: CNAPP embraces containerization technologies like Docker and Kubernetes, enabling applications to be packaged and deployed as lightweight, portable, and scalable containers.
b) Microservices Architecture: CNAPP supports the design and deployment of applications using a microservices architecture, where complex applications are broken down into smaller, loosely coupled components. This approach enhances agility, scalability, and resilience.
c) Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC): CNAPP promotes the use of infrastructure-as-code practices, allowing developers to define and manage infrastructure resources using code. Infrastructure provisioning tools like Terraform and AWS CloudFormation are commonly used.
2. Application
Focuses on securing the application layer, encompassing the code, libraries, and dependencies that make up the application. It aims to protect against application-level vulnerabilities, data breaches, and unauthorized access. Examples:
a) Secure Coding Practices: CNAPP emphasizes following secure coding practices, such as input validation, output encoding, and proper error handling, to prevent common application vulnerabilities like cross-site scripting (XSS) and SQL injection.
b) Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP): Security controls are embedded within the application runtime environment. This allows the application to defend itself against attacks, detect anomalies, and apply security policies dynamically.
c) Web Application Firewalls (WAF): Provides a layer of protection against web-based attacks by inspecting and filtering incoming application traffic.
3. Protection
Concerned with safeguarding cloud native applications and infrastructure against security threats and vulnerabilities. It includes various security controls and mechanisms to prevent, detect, and respond to attacks. This includes:
a) Vulnerability Scanning: CNAPP may offer vulnerability scanning capabilities to identify and assess vulnerabilities in the application code, libraries, and dependencies. Regular scanning helps ensure that applications are free from known security weaknesses.
b) Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): CNAPP may incorporate IDPS functionality to monitor network traffic and detect and block malicious activities that could compromise the security of cloud native applications.
c) Data Encryption: CNAPP may provide data encryption capabilities to protect sensitive data at rest and in transit. Encryption ensures that data remains secure, even if unauthorized access occurs.
4. Platform
It refers to the comprehensive nature of the solution, offering a unified platform for managing and orchestrating security controls across cloud native environments. It provides a centralized dashboard and management interface for security operations.
a) Security Orchestration and Automation: CNAPP may offer security orchestration and automation features, allowing organizations to streamline security operations, automate incident response, and enforce security policies consistently.
b) Centralized Logging and Monitoring: CNAPP may include centralized logging and monitoring capabilities, aggregating logs and security events from various cloud native components for real-time visibility and analysis.
c) Compliance and Auditing: CNAPP may provide tools and features to facilitate compliance with industry regulations and standards. It enables organizations to generate audit trails, conduct security assessments, and demonstrate compliance.
⬇️ Download Gartner CNAPP Recommendations and AccuKnox Compliance White Paper
Exploring CNAPP Features and Capabilities
Cloud Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP) offers a comprehensive set of features and capabilities designed to enhance the security of cloud native applications.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
It is a crucial aspect of CNAPP that focuses on assessing and maintaining the security posture of cloud resources. CSPM enables organizations to monitor and manage their cloud infrastructure, ensuring compliance with security best practices and industry regulations. It helps identify misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and potential risks in cloud environments.
Examples of CSPM in action include:
- Continuous monitoring of cloud infrastructure for security misconfigurations.
- Automated remediation of identified security issues to maintain a secure posture.
- Integration with threat intelligence feeds to proactively identify emerging threats.
Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) Scanning
It involves the assessment of code and configuration files used to provision and manage cloud infrastructure resources. IaC scanning helps identify security vulnerabilities and compliance issues early in the development and deployment process.
Benefits of IaC scanning:
- Early detection of security flaws and misconfigurations in infrastructure code.
- Improved collaboration between development and security teams.
- Reduction in the risk of security breaches caused by insecure infrastructure deployments.
Examples of IaC scanning include::
- Scanning Infrastructure-as-Code templates (e.g., AWS CloudFormation, Terraform) for security best practices.
- Automated checks for insecure configurations and deprecated resources.
Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP)
It focuses on securing workloads and applications deployed in cloud environments and provides visibility, threat detection, and protection mechanisms to safeguard cloud workloads from various security threats.
Real-world use cases of CWPP include:
- Protecting containerized applications in Kubernetes clusters from unauthorized access and malicious activities.
- Securing serverless functions by implementing access controls, encryption, and runtime security measures.
Cloud Service Network Security (CSNS)
CSNS targets securing the network connectivity and communication between cloud services and resources. It ensures that data transfers within the cloud environment are protected and unauthorized access is prevented.
How does it help?
- Establishing secure communication channels between cloud services to prevent eavesdropping and data interception.
- Implementing access controls and encryption measures to protect data in transit.
- Monitoring network traffic for suspicious activities and potential threats.
Case studies showcasing CSNS implementation can demonstrate:
- Secure communication between microservices within a cloud native application architecture.
- Protection of data exchanged between different cloud services (e.g., between an application and a database).
Kubernetes Security Posture Management (KSPM)
KSPM focuses specifically on securing Kubernetes environments, which are widely used for deploying and managing containerized applications and helps organizations assess and enhance the security of their Kubernetes clusters and workloads.
The relevance of KSPM in securing Kubernetes environments is notable in the following scenarios:
- Assessing the configuration of Kubernetes clusters to identify vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
- Monitoring Kubernetes resources for security risks and compliance violations.
- Providing visibility into containerized workloads and ensuring their security throughout the application lifecycle.
Instances where KSPM proves valuable:
- Detecting and remedying insecure container configurations, such as running containers with excessive privileges or using vulnerable container images.
- Monitoring and managing access controls and permissions within Kubernetes clusters to prevent unauthorized access and privilege escalation.
- Conducting runtime security assessments to identify suspicious or malicious activities within containerized workloads.
- Ensuring compliance with Kubernetes security best practices and industry regulations.
- Integrating with threat intelligence feeds to proactively identify and mitigate potential security threats.
💡Ready to elevate your Kubernetes workload security to the next level? Read our in-depth case study here and discover the power of KubeArmor, the leading Zero Trust security platform designed specifically for Kubernetes environments. With KubeArmor, you can confidently protect your workloads in the cloud while exploring new possibilities in edge computing, IoT, data on Kubernetes (DoK), and 5G control plane security.
Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM)
Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM) focuses on managing and securing entitlements within cloud environments and involves controlling access privileges, permissions, and roles associated with cloud resources to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
The significance of CIEM in managing cloud entitlements includes:
- Implementing least privilege principles to limit access to only necessary resources and actions.
- Regularly reviewing and auditing access permissions to identify and revoke excessive privileges.
- Monitoring and detecting unusual or suspicious access patterns that may indicate compromised accounts or insider threats.
Practical examples of CIEM implementation include:
- Enforcing strong access controls and policies for cloud resources, such as storage buckets, virtual machines, and databases.
- Automating access reviews and certification processes to ensure ongoing compliance with security policies.
- Integrating CIEM with identity and access management (IAM) solutions to centralize and streamline entitlement management.
Integration to Software Development Activities
Integrating CNAPP with software development activities is crucial for enhanced security throughout the application development lifecycle. It involves integrating security controls, testing, and monitoring mechanisms into the software development process to identify and address security vulnerabilities early.
Benefits of seamless integration:
- Early identification and resolution of security issues during development and testing phases.
- Continuous security testing and monitoring of application components.
- Improved collaboration between development, security, and operations teams.
By integrating CNAPP with software development activities, organizations can:
- Implement security testing frameworks, such as static application security testing (SAST) and dynamic application security testing (DAST).
- Automate security checks and vulnerability scanning as part of the continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipeline.
- Incorporate security requirements and best practices into the software development process through secure coding guidelines and secure design principles.
💡Intrigued? Ready to take your security to the next level? Experience the simplicity and power of AccuKnox as we bring zero trust principles to every layer of your applications and data. With our open-source, DevSecOps oriented and Shift-Left driven solutions, you can enjoy quick and cost-effective implementation while reaping the key benefits of enhanced cloud security.
Advantages of CNAPP
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, organizations face numerous security challenges when adopting cloud native applications. Deploying and managing these applications securely requires a robust solution that can effectively mitigate risks and protect valuable assets. This is where a Cloud Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP) comes into play, offering a range of advantages that empower DevSecOps teams to enhance their security posture and achieve their goals efficiently.
Comprehensive Security: CNAPP provides end-to-end security coverage, addressing the unique challenges faced by cloud native applications. It encompasses a wide range of security capabilities, including vulnerability management, threat detection, access control, and data protection, ensuring holistic protection for your applications and infrastructure.
Scalability and Flexibility: CNAPP is designed to seamlessly scale alongside your cloud native environment. Whether you are expanding your application footprint or migrating to different cloud providers, CNAPP offers the flexibility to adapt and secure your evolving infrastructure, saving time and effort in managing security across multiple platforms.
Streamlined DevSecOps Workflow: CNAPP integrates seamlessly into the DevSecOps workflow, enabling security considerations to be incorporated throughout the software development lifecycle. With automated security controls, policy enforcement, and continuous monitoring, CNAPP empowers developers to build and deploy applications securely, without sacrificing agility and productivity.
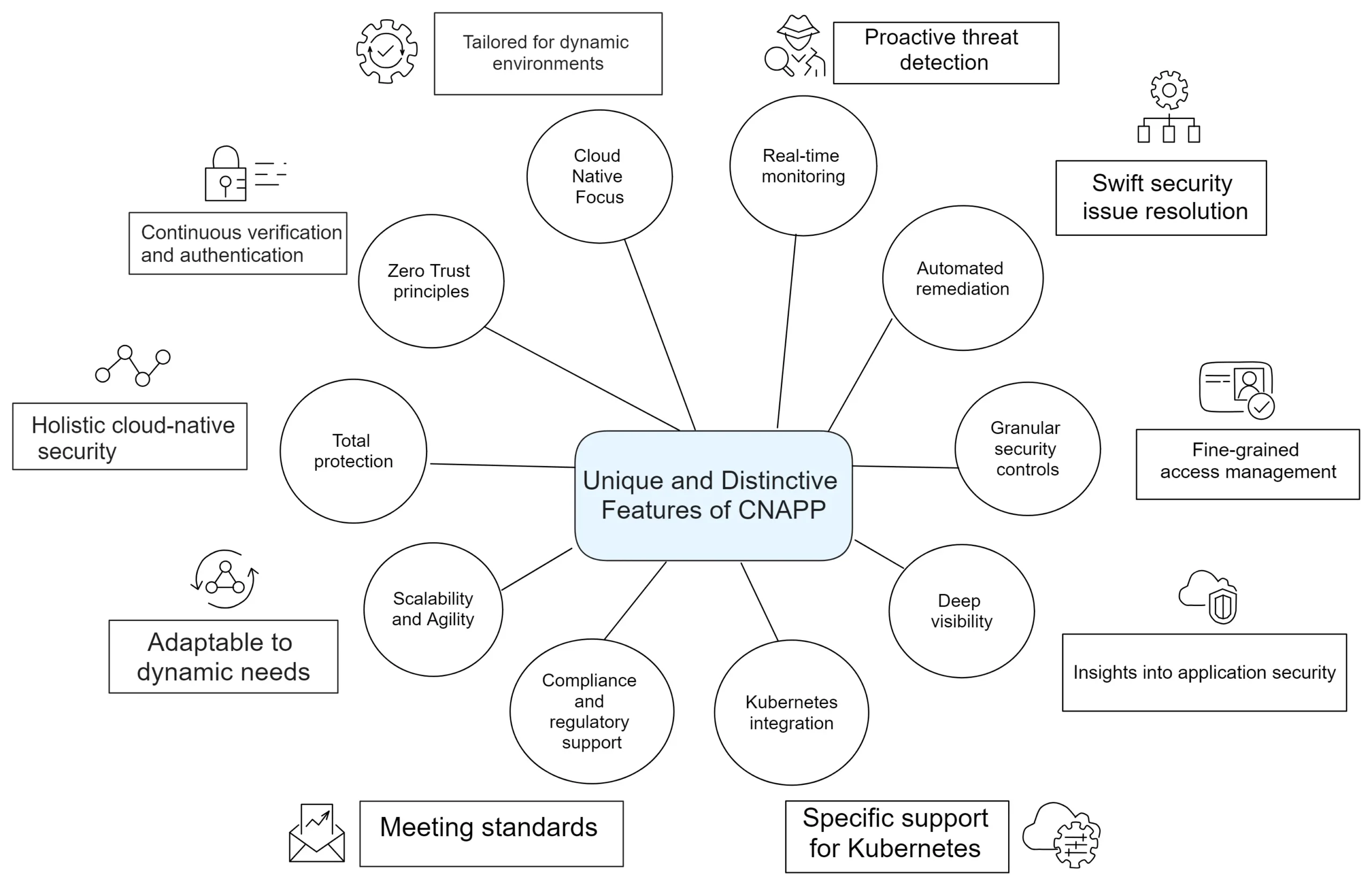
Specific advantages in addressing security challenges
Proactive Threat Mitigation: CNAPP leverages advanced threat intelligence and behavioral analysis to detect and mitigate threats proactively. It helps identify vulnerabilities, suspicious activities, and potential attack vectors, allowing DevSecOps teams to take preemptive action before any significant security incidents occur.
Compliance and Regulatory Alignmentt: CNAPP assists organizations in achieving compliance with industry regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. It provides robust controls, audit trails, and reporting mechanisms to demonstrate adherence to security and privacy requirements, avoiding hefty fines and reputational damage.
Enhanced Visibility and Control: CNAPP offers deep visibility into your cloud native environment, providing real-time insights into application behavior, network traffic, and user access. This visibility enables you to identify anomalies, enforce access controls, and respond swiftly to potential security incidents, bolstering your overall security posture.
Case studies demonstrating the advantages of CNAPP adoption
- Organizations are securing their cloud native applications with CNAPP, reducing the number of security incidents by 70% and achieving compliance with industry regulations. By leveraging the comprehensive security features and streamlined workflow of CNAPP, they effectively protect their critical assets while maintaining operational efficiency.
- DevOps Teams adopt CNAPP to strengthen their security posture in a rapidly expanding cloud native environment. With CNAPP’s scalability and flexibility, they seamlessly integrate security into their workflow, enabling faster deployment cycles and reducing time spent on security maintenance.
- Subject matter experts successfully mitigate a sophisticated cyberattack using CNAPP’s proactive threat detection capabilities. By leveraging the comprehensive threat intelligence and automated response mechanisms of CNAPP, they thwart the attack and minimize the potential impact on their business operations.
These case studies and success stories exemplify the practical advantages and positive outcomes that can be achieved through the adoption of CNAPP, providing DevSecOps teams with concrete evidence of its effectiveness in securing cloud native applications.
Transforming Cloud Native Security: AccuKnox Zero Trust CNAPP Platform
AccuKnox is at the forefront of providing advanced Cloud Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP) solutions. With our deep understanding of cloud security, we offer a comprehensive CNAPP solution designed to safeguard cloud native applications against emerging threats and vulnerabilities. Built on open-source innovations, our CNAPP solution ensures reliable and effective security measures for organizations looking to secure their cloud native environments.
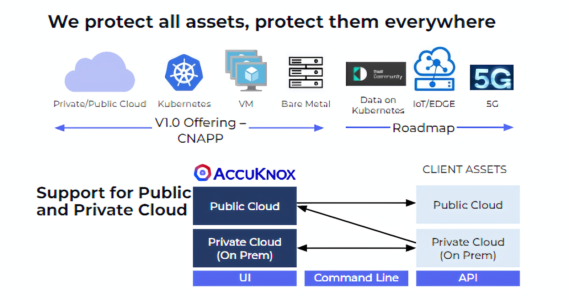
AccuKnox’s approach to Zero Trust CNAPP
At AccuKnox, we take a comprehensive and proactive approach to cloud native application protection. Our focus is on applying zero trust principles across all layers, from identity and network to the application and data layers. By leveraging advanced technologies and techniques, we provide comprehensive security coverage across the entire cloud native application stack. This approach ensures that our customers’ cloud native applications remain secure and resilient in dynamic and distributed environments.
Key features and benefits of Zero Trust CNAPP offered by AccuKnox
At AccuKnox, our mission is to equip organizations with the necessary tools and capabilities to effectively protect their cloud native applications. We prioritize delivering cutting-edge security measures, enabling businesses to embrace the benefits of cloud native architectures while ensuring the highest level of protection and resilience against evolving threats and vulnerabilities.
- Comprehensive Zero Trust Cloud Native Security Platform
- Basic offering includes Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) and Kubernetes Security Posture Management (KSPM)
- Advanced features provided by Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP)
- Backed by the strength of KubeArmor with 500,000+ downloads and 500 stars
- Support for Public, Multi-Cloud, and Private Clouds (on-premises)
- Secure modern (Kubernetes) and traditional (Virtual Machine) workloads
- DevSecOps-driven approach for seamless integration into development processes
- Future-proof roadmap with plans to support IoT/Edge and 5G environments
- Strong intellectual property with 10+ patents and ongoing R&D partnership
- Passionate commitment to customer satisfaction, ensuring your security needs are met
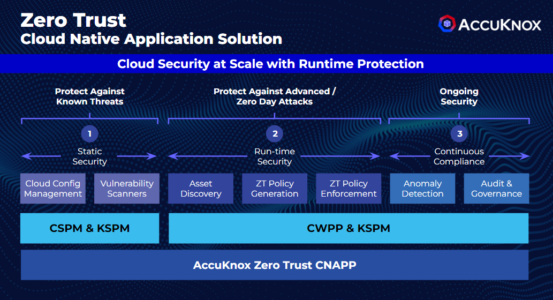
Conclusion
CNAPP represents a powerful solution for safeguarding cloud native applications, and its adoption is a vital step in ensuring comprehensive security in today’s dynamic digital landscape.
Adopting CNAPP offers numerous benefits, including enhanced security, improved compliance, and the ability to address the unique challenges faced by cloud native environments. By leveraging it, organizations can proactively mitigate security risks, protect sensitive data, and maintain the integrity of their cloud native applications.
Looking ahead, the future of CNAPP holds promise as cloud native architectures continue to evolve and expand. As organizations increasingly embrace cloud native technologies, the role of CNAPP in securing these applications will become even more critical. Businesses must recognize the importance of integrating CNAPP into their security strategies to ensure the ongoing protection and resilience of their cloud native environments.
Must read articles
- Zero Trust (ZT) – The Future of Cloud Security
- Zero Trust (ZT) Architecture, Framework and Model
- Cloud Security Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC)
- How to Pick the Right CNAPP (Cloud Native Application Protection Platform) Vendor
- What is Driving the Need for CSPM (Cloud Security Posture Management)
- Agent vs Agentless Multi Cloud Security
Zero Day Attacks cost $3.9M on average

4+
Marketplace Listings
7+
Regions
33+
Compliance Coverage
37+
Integrations Support

Stop attacks before they happen!
According to the latest IBM cloud attack report - Each cloud attack on an average costs $3.92M
Total Exposed Attacks in 2024 Costed
